Understand your soil type and trace element status
Soil type is the one of most important influential factors on trace element content. Soil type is formed based on factors including geology (parent material), climate (rainfall, temperature, humidity), organisms (organic matter for example), farm management (ploughing, liming, fertilisers, animal factors), geography (rivers, flood plains, tree types), and time.
The trace element status of individual farms, and even within individual fields, is therefore – to a degree – something that we cannot radically change when we consider all factors influencing soil type.
The impact of seasonality and weather is also something we can’t change. In simple terms, rapid growth usually means lower trace element levels due to dilution within the forage. The same would apply to the use of fertilisers and liming as these encourage growth. But for every example, there may be a counter.
That said, there are things we can do to influence the trace element status of grass. But before doing anything, it is vital that you understand your trace element status through soil, forage and even blood analysis.
Influence the trace element status of your grass
Research undertaken by SIP in association with Bangor University, showed that although pasture improvements improved grass yield, they lowered the trace element status of the pasture. Combating trace element deficiency is more than just supplementation. Effective supplementation goes together with grassland management. Here’s 3 important influencers of trace element levels in grassland:
1. Soil pH
Soil pH directly impacts on overall nutrient availability, and the optimum availability of most plant nutrients occurs over a small range of soil pH values. Lime acts as a ‘soil conditioner’ that, when applied correctly, will increase soil pH and in-turn amend any soil acidity. In this instance, liming can increase the availability of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, and can therefore encourage grass growth and even make grass more palatable to grazing animals. However, increased forage growth can also indirectly dilute trace elements, and over-liming can reduce the uptake of cobalt, copper, selenium, and manganese.
2. Sward type
Grasses that incorporate clovers along with certain broad-leaved plants and heathers are almost always richer in nitrogen and protein. Depending on soil type, some pastures containing white and red clover can also offer higher cobalt concentrations than predominantly ryegrass swards. Some swards are selected for higher yields; however, these are gradually depleting trace element reserves in the soil. A constant withdrawal of trace elements will upset the balance.
3. Fertilising strategies
Nitrogen fertiliser will boost yields but will then effectively ‘dilute’ trace element levels due to greater dry matter production. It’s important to add manure back into the soil, as it contains trace elements. Correct manure sourcing, storage, and application is vital.
Supplement to counteract trace element deficiencies
Once you understand your trace element status and have done what you can to positively influence those levels through your grassland management, it’s time to consider supplementation to counteract deficiencies. It is tempting to look for the trace element solution that offers the most in terms of value for money. However, when it comes to supplementation, target sufficiency to avoid costly deficiencies and toxicity risks. At ANIMAX, we refer to this principle as ‘enough’ – not too much and not too little.
Trace elements can be directly applied to soils or grass. However, this comes with a risk of deficiency and toxicity. For example:• Cobalt salts increases cobalt content to adequate levels but in the shorter term, and the data to support cobalt salt application is poor.• Copper salts applied to soil doesn’t increase copper content adequately. There is also the concern of run off and pollution.• Similarly to copper, selenium top-dressing may be toxic to begin with and then rapidly declines. Deaths are reported with selenium fertilisers.Direct application can be inefficient, expensive, and harmful to the environment.
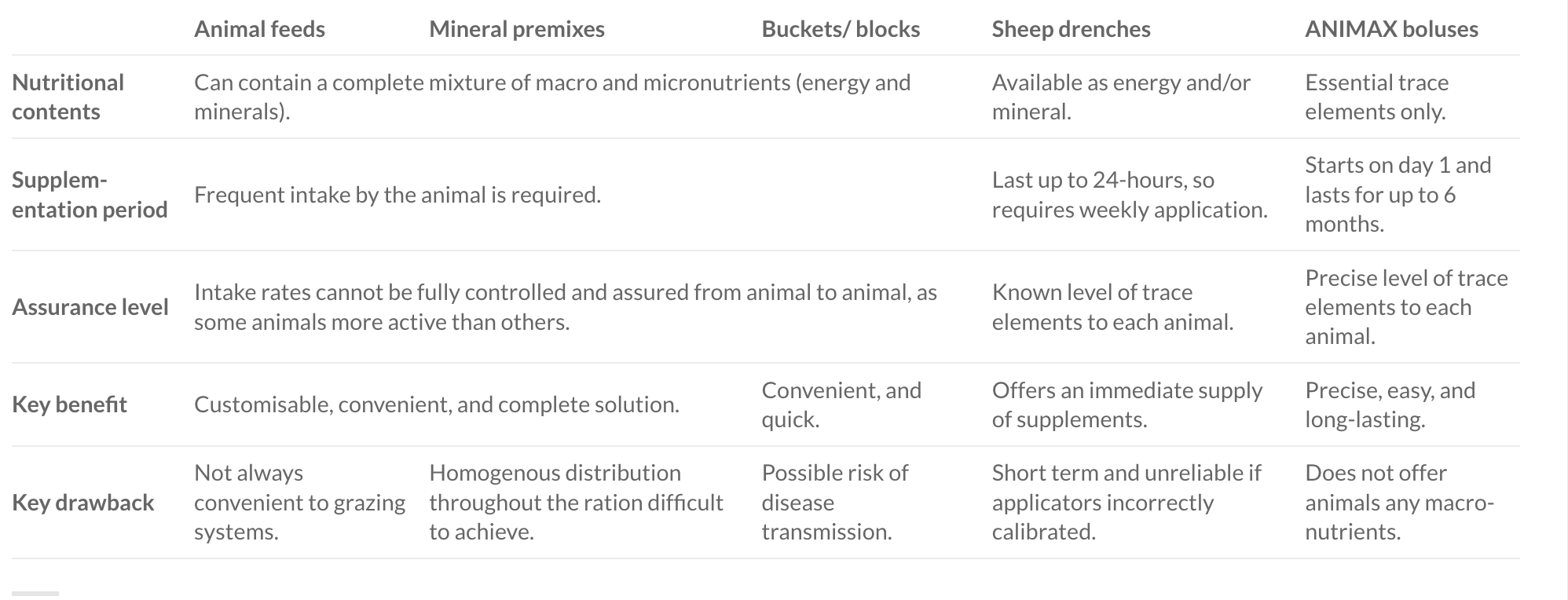
Choosing to supplement with a mineral bolus?
- Pre-breeding or pre-calving
- Pre-tupping or pre-lambing
- When worming or carrying out other management activities.
- Do they supply enough of the trace elements you are deficient in?
- Do they offer trace elements that can be absorbed in the animal?
- Will they retain size and mass to stay in the animal’s rumen?
- Will they offer at the right levels throughout the supplementation period?
- Are they easy to apply?
Interested in using a mineral bolus?
Find your local ANIMAX stockist.